Caring for Someone With Diabetes – VeryWellHealth
Click here to read the ORIGINAL ARTICLE: “Caring for Someone With Diabetes: What to Know.”
Approximately 9.4% of the U.S. population lives with diabetes. Although there is no cure, there are ways to manage diabetes and stay healthy. A caregiver can help.
By Cory Martin. Fri Sep 02, 2022
Diabetes is a chronic condition that occurs when blood sugar levels become too high. High blood sugar happens when the body produces too little to no insulin or doesn’t respond to it well. Insulin is used by the body to convert glucose (sugar) into energy for the cells.
Left untreated, diabetes can cause serious health problems such as kidney disease, nerve damage, and eye problems.
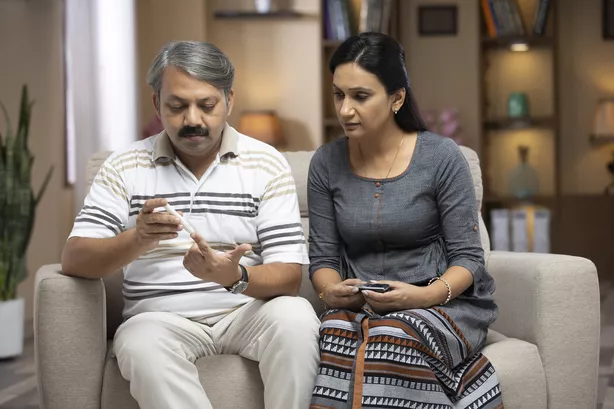
Caring for a loved one with diabetes can include administering or tracking medications, encouraging changes to diet and activity levels, and ensuring regular monitoring by a healthcare provider.
This article covers what you need to know about diabetes, your responsibilities as a caregiver of someone with diabetes, what you should try to avoid, how to talk to your loved one with diabetes, and how to take care of yourself as a caregiver.
What You Need to Know About Diabetes

Diabetes is a lifelong condition that requires ongoing management to control blood sugar levels. There are several types of diabetes. The most common types are type 1, type 2, and gestational. They are:
- Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks the pancreas and the body stops producing insulin. People with type 1 require insulin daily to survive.
- Type 2 diabetes occurs when the body does not make or use insulin well. Some people may require insulin with type 2.
- Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and often goes away after birth.
Signs and symptoms of diabetes include:
- Extreme thirst
- Hunger even after eating
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Frequent infections or slow-healing cuts/sores
- Weight loss even with increased eating
- Numbness, tingling, or pain in the hands or feet
Once someone is diagnosed with diabetes, a healthcare provider will develop a treatment plan.
Treatment for diabetes includes using devices to monitor blood glucose levels, medications such as insulin and Glucophage (metformin) to control blood sugar levels, and lifestyle modifications such as diet and exercise.